A Guide to Different Types of Heavy Vehicle Engine Parts
A Guide to Different Types of Heavy Vehicle Engine Parts
The heavy vehicle industry is an essential part of the global economy, as it is responsible for the transportation of goods and materials across various industries. Heavy vehicles are equipped with powerful engines that are designed to withstand the demands of heavy loads and long distances. However, these engines are made up of various parts that need to be maintained and replaced to ensure their proper functioning. In this essay, we will be discussing the different types of heavy vehicle engine parts and their functions.
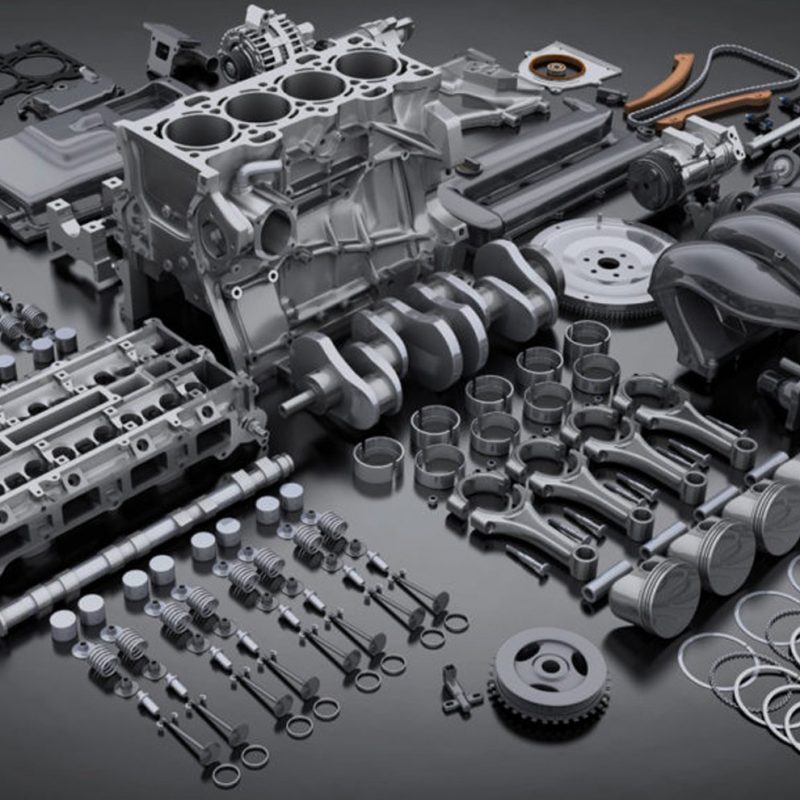
- Cylinder Block – The cylinder block is the main structural component of the engine and houses the cylinders, in which the combustion process takes place. It is typically made of cast iron or aluminum and is designed to withstand the high pressures and temperatures generated by the combustion process.
- Cylinder Head – The cylinder head sits on top of the cylinder block and forms the combustion chamber. It also contains the valves, which control the flow of air and fuel into the engine and the exhaust gases out of the engine. The cylinder head is typically made of aluminum or cast iron and must be able to withstand the high temperatures and pressures generated by the combustion process.
- Pistons – The pistons are located inside the cylinders and move up and down to convert the energy generated by the combustion process into mechanical energy. They are typically made of cast aluminum or forged steel and are designed to withstand the high temperatures and pressures generated by the combustion process.
- Connecting Rods – The connecting rods connect the pistons to the crankshaft and convert the reciprocating motion of the pistons into rotational motion. They are typically made of forged steel and are designed to withstand the high forces generated by the combustion process.
- Crankshaft – The crankshaft is located at the bottom of the engine and converts the reciprocating motion of the pistons into rotational motion. It is typically made of forged steel and is designed to withstand the high forces generated by the combustion process.
- Camshaft – The camshaft is located in the cylinder head and controls the opening and closing of the valves. It is typically made of cast iron or steel and is designed to withstand the high temperatures and pressures generated by the combustion process.
- Timing Chain or Belt – The timing chain or belt is responsible for synchronizing the movement of the camshaft and crankshaft. It is typically made of metal or reinforced rubber and is designed to withstand the high temperatures and pressures generated by the combustion process.
- Valvetrain – The valvetrain is responsible for opening and closing the valves and is typically made up of rocker arms, push rods, and lifters. It is typically made of steel or aluminum and is designed to withstand the high temperatures and pressures generated by the combustion process.
- Oil Pump – The oil pump is responsible for circulating oil throughout the engine to lubricate and cool the moving parts. It is typically made of metal and is designed to withstand the high temperatures and pressures generated by the combustion process.
- Cooling System – The cooling system is responsible for keeping the engine at the proper temperature. It is typically made up of a radiator, water pump, and thermostat, and is designed to withstand the high temperatures generated by the combustion process.
In conclusion, heavy vehicle engines are made up of various parts that work together to power the vehicle. These parts include the cylinder block, cylinder head, pistons, connecting rods, crankshaft, camshaft, timing chain or belt, valvetrain, oil pump, and cooling system. It is important for heavy vehicle owners to understand the functions of these parts and to regularly maintain and replace them as needed to ensure the proper functioning of the